Inflammation and DNA repair are crucial biological processes. They are intimately linked, impacting our health significantly. Glutathione, a key molecule, plays a vital role in both processes. This article explores the significance of maintaining adequate glutathione levels for controlling inflammation and aiding in DNA repair.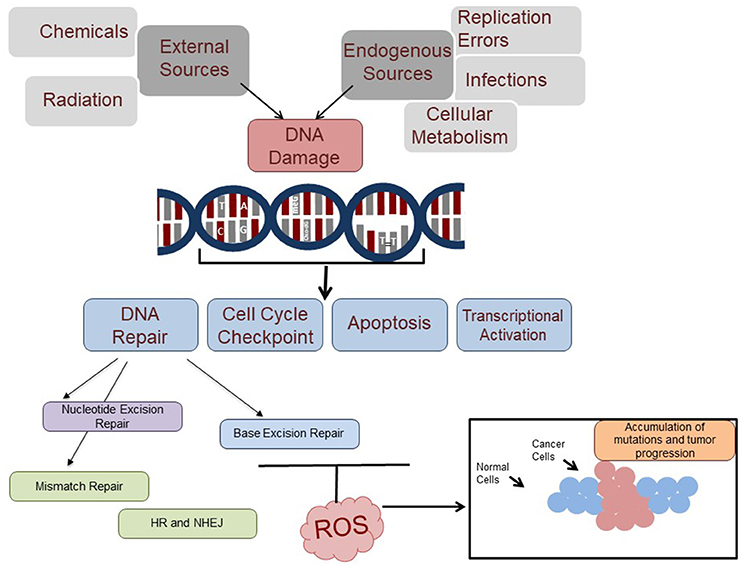
Understanding Inflammation and DNA Repair
DNA damage triggers inflammation. When DNA is damaged, pathways like NF-κB activation lead to inflammation and cellular aging. This process affects DNA repair mechanisms and can lead to diseases like cancer. Chronic inflammation further hampers DNA repair, creating a damaging cycle.
The Role of Glutathione
Glutathione, a potent antioxidant, is crucial in our body. It reduces oxidative stress, protecting cells from DNA damage. It assists in DNA repair and mitigates inflammation. This function is vital for cellular health and longevity.
Glutathione and Age-Related Changes
Aging influences DNA repair and inflammation. As we age, glutathione levels can decline, leading to increased inflammation and reduced DNA repair capacity. Maintaining glutathione levels is essential for healthy aging and preventing age-related diseases.
Enhancing Glutathione Levels for Better Health
Dietary sources like fruits and vegetables can boost glutathione levels. Supplements and lifestyle changes, such as reducing stress, also help. These efforts enhance DNA repair and reduce inflammation, promoting overall health.
Practical Implications and Future Directions
Glutathione’s role in health is a growing research area. It has potential therapeutic applications for diseases related to DNA damage and inflammation. Future research will further elucidate glutathione’s role in our bodies.
Conclusion
Maintaining adequate glutathione levels is key for controlling inflammation and aiding DNA repair. This balance is crucial for health and longevity.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How does DNA damage contribute to inflammation?
DNA damage can lead to inflammation through several pathways. One key mechanism is the activation of NF-κB by DNA damage independently of cGAS, a DNA sensor. This activation leads to inflammation and senescence, inhibiting autophagy of GATA4, a transcription factor involved in cellular growth and development.
What is the role of glutathione in DNA repair and inflammation control?
Glutathione, a potent antioxidant, plays a crucial role in reducing oxidative stress and thereby protecting cells from DNA damage. It helps in the repair of damaged DNA and controls inflammation by neutralizing free radicals and other reactive oxygen species that can damage cellular components.
Can maintaining adequate glutathione levels reduce age-related inflammation?
Yes, maintaining adequate glutathione levels can mitigate age-related inflammation. Glutathione deficiency is linked to increased oxidative stress and impaired DNA repair mechanisms, leading to cellular aging and inflammation. Supplementing glutathione levels can help reduce these effects and promote healthy aging.
What are the consequences of DNA damage-induced inflammation?
DNA damage-induced inflammation can lead to various consequences, including cellular senescence, immune system activation, and potentially, the development of chronic diseases like cancer. Persistent DNA damage signaling triggers senescence-associated inflammatory cytokine secretion, contributing to the aging process and age-related diseases.
How does inflammation affect DNA repair processes?
Inflammation can impact DNA repair processes in several ways. Inflammatory cytokines and oxidative stress can hinder the efficiency of DNA repair mechanisms. Additionally, chronic inflammation can lead to an environment conducive to further DNA damage, creating a cycle of damage and inadequate repair.
What strategies can be employed to enhance glutathione levels and DNA repair capacity?
Strategies to enhance glutathione levels and DNA repair capacity include dietary changes to include glutathione-rich foods, supplementation with glutathione precursors like N-acetylcysteine, and lifestyle modifications to reduce oxidative stress. These strategies can help maintain optimal glutathione levels, thereby supporting efficient DNA repair and reducing inflammation.
References